Introduction to IELTS Task 2 Essay Types
One of the biggest sources of confusion in IELTS Writing Task 2 is not vocabulary, grammar, or ideas. It is recognising what type of essay the question is asking for. Many candidates lose marks not because their English is weak, but because they respond in the wrong way to the task.
This is why understanding IELTS Task 2 essay types is such an important foundation skill. When you correctly identify the essay type, your structure becomes clearer, your paragraphs become more logical, and your score becomes more predictable.
This lesson will explain all major Task 2 essay types in clear, practical terms. Rather than memorising rigid templates, you will learn how each essay type thinks, what examiners expect from it, and how the logic changes from one type to another.
Join over 500+ learners
Join the community for free resources and other learning opportunities.
No spam — only valuable English learning content.
Why Essay Type Matters More Than You Think
Examiners assess Task 2 essays primarily on Task Response and Coherence. Both of these depend heavily on whether you have understood the question correctly.
Two candidates can write essays with similar language level, but receive very different scores if one has matched the essay type accurately and the other has not. Writing a strong opinion essay in response to a discussion question, for example, often results in a Band 6.5 ceiling.
Essay type is therefore not a technical detail. It is the framework that everything else sits on.
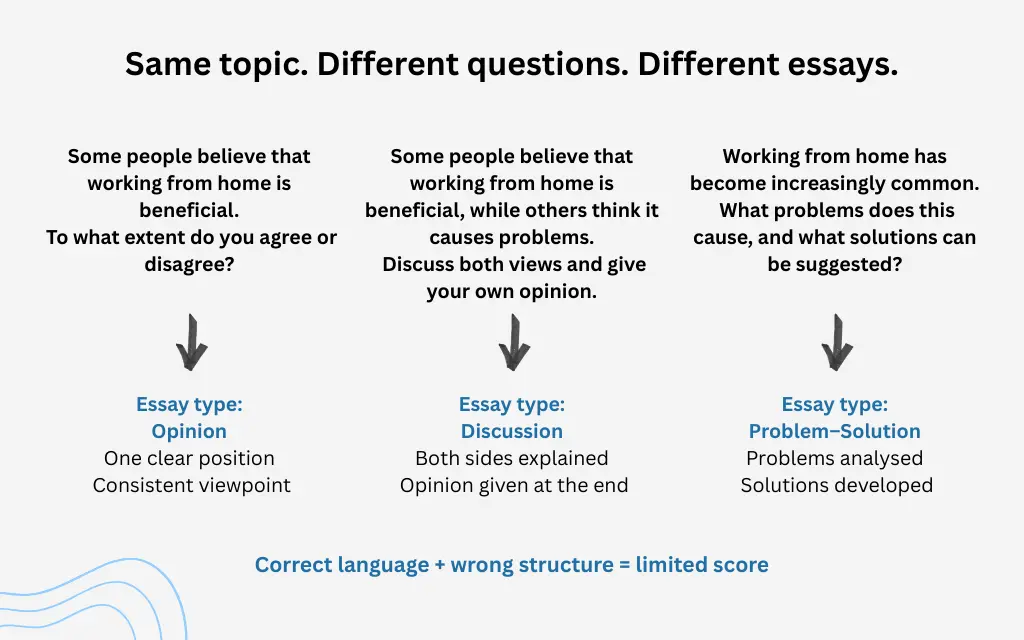
The Core IELTS Task 2 Essay Types
Although Task 2 questions look varied, most of them fall into a small number of recognisable essay types. These types are defined by what the question asks you to do, not by the topic itself.
Understanding this allows you to focus on logic rather than memorisation.
Opinion Essays (Agree / Disagree)
Opinion essays are among the most common Task 2 questions. They usually ask whether you agree or disagree with a statement, or to what extent you agree.
The key feature of this essay type is position. Examiners expect you to take a clear stance and maintain it throughout the essay. Ambiguity here often leads to weaker Task Response scores.
A strong opinion essay introduces the topic, states a clear view, and then supports that view logically in the body paragraphs. Balance is allowed, but clarity comes first.
Many candidates struggle with opinion essays because they try to appear neutral. In IELTS, neutrality is not required unless the question explicitly asks for it.
Discussion Essays (Discuss Both Views)
Discussion essays are often confused with opinion essays, but they require a different approach.
These questions typically ask you to discuss two opposing views. Sometimes they also ask for your opinion, but sometimes they do not. Reading the final line of the question carefully is essential.
In a pure discussion essay, examiners expect you to explore both sides fairly. Each main body paragraph usually focuses on one view, explaining it clearly before moving on.
When an opinion is required, it is often introduced briefly in the introduction and confirmed in the conclusion, rather than dominating the body paragraphs.
Advantage and Disadvantage Essays
Advantage–disadvantage essays focus on evaluation rather than argument. The question usually asks whether the benefits outweigh the drawbacks, or simply to discuss both.
The logic of this essay type is comparative. One part of the essay explores positive aspects, and another explores negative aspects.
A common mistake is treating this like an opinion essay and arguing strongly for one side. While judgement may be required, the primary goal is to show clear understanding of both sides of the issue.
Examiners value clarity and balance here more than persuasion.
Problem and Solution Essays
Problem–solution essays ask you to analyse an issue and suggest ways to address it.
These questions usually include words such as problem, cause, solution, or measure. The structure is often predictable, but the logic must still be clear.
A strong problem–solution essay clearly separates what is causing the problem from how it can be solved. Mixing these ideas within the same paragraph often weakens coherence.
Examiners are not judging the realism of your solutions. They are judging how clearly and logically you present them.
Cause and Effect Essays
Cause–effect essays are closely related to problem–solution essays, but they focus more on explanation than action.
These questions ask why something happens, what results from it, or both. The key here is logical connection.
A common weakness at lower bands is listing causes or effects without explaining how they connect. Band 7+ essays show clear relationships between ideas.
Cause–effect essays reward calm explanation and controlled reasoning rather than dramatic language.
Two-Part (Direct Question) Essays
Two-part questions are often underestimated. They usually ask two separate but related questions in the same task.
The challenge here is balance. Each question must be answered clearly. Candidates often focus heavily on one part and rush the other, which limits Task Response.
A clear structure is essential. Each body paragraph usually addresses one question directly, rather than mixing ideas.
This essay type tests planning more than language level.
Mixed or Hybrid Questions
Some Task 2 questions combine elements of different essay types. For example, a question might ask you to discuss a problem and give your opinion on a solution.
These questions can be challenging, but they are not designed to trick you. The key is to break the question into parts and ensure each part is addressed somewhere in the essay.
Examiners reward clarity and coverage more than sophistication in these cases.
How Essay Type Affects Introductions and Conclusions
Each essay type slightly changes how introductions and conclusions are written.
Opinion essays usually state a position early and restate it clearly at the end.
Discussion essays often introduce both views and summarise them in the conclusion.
Problem–solution essays usually signal structure in the introduction and reflect solutions at the end.
Understanding essay type helps these sections feel natural rather than forced.
Common Essay Type Mistakes That Lower Scores
Several mistakes appear repeatedly across Task 2 essays.
One is identifying the essay type incorrectly. Another is answering only part of the question. A third is using the same structure for every essay regardless of task.
These mistakes are not grammar problems. They are question analysis problems. Once candidates learn to slow down and identify the task correctly, scores often improve quickly.
Using Essay Types as a Planning Tool
Essay types are not templates. They are planning tools.
Once you know the essay type, you can decide:
- What your paragraphs should focus on
- How ideas should be grouped
- Where your position should appear
This reduces stress and makes writing under time pressure more manageable.
Conclusion
Understanding IELTS Task 2 essay types is one of the most effective ways to improve writing scores. It aligns your response with examiner expectations and allows your language ability to show more clearly.
By learning how opinion, discussion, advantage–disadvantage, problem–solution, and other essays work, you gain control over structure rather than guessing what the question wants.
To develop each essay type in more depth, explore the related Learn English Weekly guides linked below, where each type is broken down step by step.
Related IELTS Task 2 Lessons
Glossary
Essay type (noun) — The structure required by a Task 2 question
Opinion (noun) — A personal view or stance
Discussion (noun) — Consideration of multiple viewpoints
Task Response (noun) — How well the essay answers the question
Structure (noun) — The organisation of ideas in an essay
Practice Questions
- True or False: Essay type depends on the topic.
- Which essay type requires the clearest position?
A) Discussion
B) Opinion - Why are two-part questions challenging?
- Short answer: Name one common Task 2 essay type.
- True or False: All Task 2 essays use the same structure.
Answers
- False
- B
- Because both questions must be answered clearly
- Opinion / Discussion / Problem–Solution / Advantage–Disadvantage
- False
Join over 500+ learners
Join the community for free resources and other learning opportunities.
No spam — only valuable English learning content.
