Introduction to IELTS Listening Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple choice questions look familiar.
You have seen them at school.
You have answered them in practice books.
They appear straightforward.
Yet IELTS listening multiple choice questions are often where strong candidates lose valuable marks.
The difficulty is not vocabulary alone. It is precision. It is interpretation. And above all, it is your ability to recognise listening distractors while the recording continues.
This lesson will explain how MCQ listening IELTS tasks are structured, why they feel challenging, and how to approach them strategically for higher band performance.
Join over 500+ learners
Join the community for free resources and other learning opportunities.
No spam — only valuable English learning content.
What Are Multiple Choice Questions in IELTS Listening?
In IELTS Listening, multiple choice questions require you to select the correct answer from a list of options. You may see:
- Three options (A, B, C)
- Four options (A, B, C, D)
- A single correct answer
- Occasionally, a question requiring more than one answer
Unlike form completion, you are not copying words directly from the recording. Instead, you must understand meaning, compare ideas, and identify which option accurately reflects the speaker’s final message.
Multiple choice questions appear in all sections but are especially common in:
- Section 3 (academic discussion)
- Section 4 (academic lecture)
These sections involve reasoning, explanation, and opinion shifts, which naturally suit the multiple choice format.
Why IELTS Listening Multiple Choice Feels Difficult
The challenge is rarely speed alone.
The real difficulty lies in similarity.
The options often look very close in meaning. You may hear information connected to all three choices. However, only one reflects the speaker’s final, confirmed idea.
Consider this example:
Question: Why did the student change her research topic?
A. It was too expensive.
B. It was too complicated.
C. It lacked available sources.
In the recording, the student might say:
“At first I was worried about funding, but the real issue was that the topic became far more complex than I expected.”
All three ideas may be mentioned. Only one matches the final reason.
This is how listening distractors work.
Understanding Listening Distractors
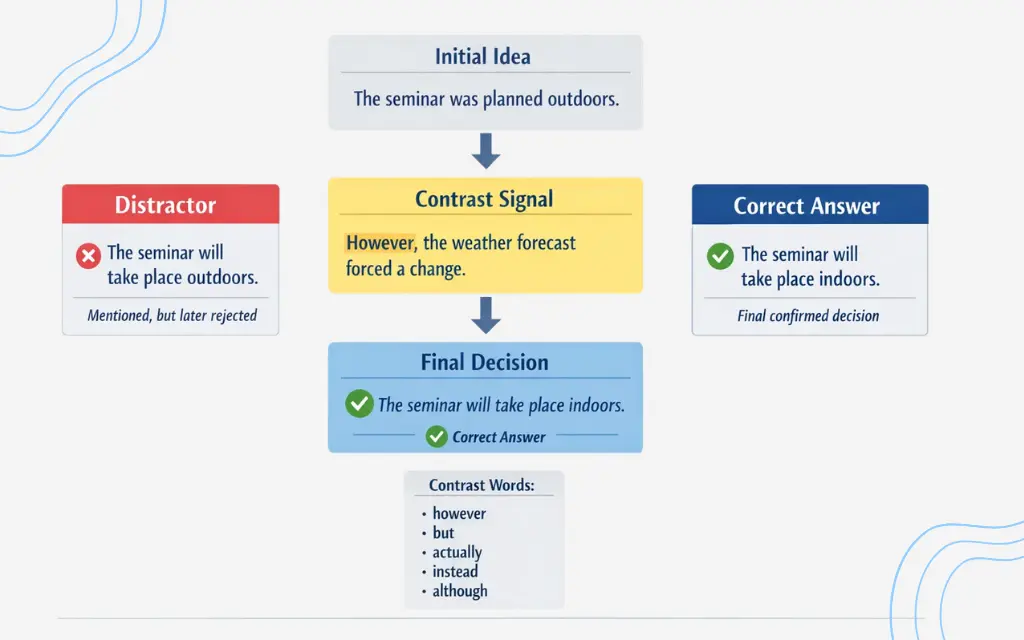
A distractor is an option that is mentioned but later rejected, corrected, or modified.
For example:
“We originally planned to hold the seminar outdoors. However, the weather forecast forced us to move it inside.”
If an option says “The seminar will take place outdoors”, that is a distractor. It appears in the recording, but it is not correct.
Why Distractors Are Effective
Distractors test whether you:
- Stop listening too early
- React to keywords instead of full meaning
- Fail to notice contrast signals such as however, but, or actually
In IELTS listening multiple choice, the correct answer usually reflects the final decision or confirmed opinion, not the first idea mentioned.
Listening for Meaning, Not Keywords
Many candidates underline keywords in the options and wait to hear them repeated.
This helps at a basic level. However, IELTS rarely repeats wording exactly.
For example:
Option: “The lecture was too demanding.”
Recording: “The workload was overwhelming.”
The meaning matches. The vocabulary does not.
Recognising paraphrasing is essential for MCQ listening IELTS tasks. You must train yourself to listen for ideas rather than isolated words.
How to Use Preparation Time Effectively
Before the recording begins:
- Read the question carefully.
- Compare all options closely.
- Identify the small differences between them.
For example:
A. He enjoyed the lecture.
B. He found the lecture useful.
C. He found the lecture confusing.
Enjoyment and usefulness are not identical. The speaker may value something without enjoying it.
By predicting what you are listening for, you reduce cognitive pressure once the recording starts.
Tracking Idea Development in Section 3 and 4
Multiple choice questions are particularly common in academic discussion listening contexts.
In Section 3, speakers often:
- Introduce an idea
- Question it
- Replace it with a revised decision
For example:
“I thought the survey results were reliable at first, but after reviewing the data again, I realised there were major flaws.”
The correct answer reflects the final evaluation, not the initial reaction.
In Section 4, the lecturer may present several theories before explaining which one is most widely accepted. Again, the final position is what matters.
Listening carefully for contrast words such as however, instead, in fact, and on reflection helps you identify these shifts.
Managing Uncertainty During the Recording
Multiple choice questions can feel stressful because the information moves quickly.
If you miss a detail:
- Stay focused on the current question.
- Listen for clarification or restatement.
- Avoid replaying missed information in your mind.
Sometimes the speaker explains the idea again in different words. Losing concentration after one missed sentence often leads to further mistakes.
Precision and calm thinking are more important than speed.
How Multiple Choice Influences Your IELTS Listening Band Score
Multiple choice questions often carry several marks in a single section. Losing control of distractors can quickly reduce your raw score.
However, once you develop the habit of:
- Listening for final decisions
- Recognising paraphrasing
- Identifying contrast signals
your accuracy improves noticeably.
Strong candidates are not necessarily faster listeners. They are more controlled listeners.
Conclusion
IELTS listening multiple choice questions test more than vocabulary recognition.
They assess:
- Your ability to compare similar ideas
- Your awareness of listening distractors
- Your understanding of paraphrasing
- Your focus on final meaning
If you train yourself to follow full idea development rather than reacting to individual words, your confidence and band score will increase steadily.
Understanding distractors is one of the clearest pathways to Band 7 and beyond.
Related IELTS Listening Lessons
- Distractors in IELTS Listening (Why Answers Change)
- IELTS Listening Section 3 Explained
- Common IELTS Listening Mistakes (And How to Avoid Them)
Glossary
Multiple Choice (n.)
A question type where you select the correct answer from several options.
Distractor (n.)
An incorrect option that is mentioned or sounds similar to the correct idea.
Paraphrasing (n.)
Expressing the same meaning using different words.
Contrast Signal (n.)
A word or phrase such as however that indicates a change in idea.
Precision (n.)
Accuracy and careful interpretation of meaning.
Practice Section
(MCQ) A distractor is:
A. The correct answer
B. A repeated word
C. An incorrect option mentioned in the recording
D. A spelling mistake
(True/False) The correct answer is usually the first idea mentioned.
(Short Answer) Why is recognising paraphrasing important in IELTS listening multiple choice?
(MCQ) Which word often signals a change in idea?
A. Firstly
B. However
C. Also
D. Similarly
(True/False) In IELTS Listening, you can replay the recording.
Answers
C
False
Because speakers often use different words to express the same meaning as the correct option.
B
False
Join over 500+ learners
Join the community for free resources and other learning opportunities.
No spam — only valuable English learning content.
